With apologies to David Letterman’s signature skit series of a decade+ ago, Charlie Green and I wrote an article with this original title for the FCPA Blog back in January 2019. After recently speaking with Charlie, the title is being borrowed again to highlight (and update) a few of the many misunderstandings about the nature of trust in business. (This updated article could also be called Trust 101: Back to Basics Again.)
Here’s our list of Five Stupid Ideas About Trust in Business, followed by some comments about the flaws.
Do these flawed views of trust merit actually being called “stupid”? You be the judge.
1. Trust is synonymous with “check-the-box” ESG, DE&I, sustainability, “greening” your organization, etc.
2. Blockchain is a road to trust.
3. Loading up corporate communications with trust words du jour elevates brand or organizational trust.
4. Elevating data security is a pathway to trust.
5. Trust can be chemically induced.
While all these ideas represent flawed views of trust, they are not all “wrong” in the same way. Exploring how they are flawed tells us a lot about what real trust concepts, tools and metrics look like.
In each case that follows, we’ll explore the flaw in the concept; then we’ll give a proactive definition of trust and some valid metrics for evaluating it.
Trust-as-ESG, DEI, sustainability, etc. If your business is promoting equality and sustainable practices, good for you. You may also be creating some positive vibes for your brand, and even — dare we say — being rewarded in the real for-profit world for doing so. But don’t confuse these actions with trust. The most powerful form of trust is personal, not institutional. Policies — whether for equality, sustainability or money-laundering for that matter — are about as impersonal as you can get.
Second, if you are indeed making money by, for example, being sustainable, congratulations — but you’re also raising questions about your motives. If you’re “doing good” in order to be “doing well,” then your motives are suspect, and are actually reasons for most people not to trust you.
Blockchain. First, count us among those who see the virtues of blockchain quite apart from its dubious connections to digital currencies — certainly Bitcoin. Blockchain is a legitimate and powerful tool, with valid applications that are only beginning to be scoped out. Emerging technology always comes with unanticipated risk. That said, blockchain doesn’t enable “trust” — it brings clarity and efficiency to the anti-fraud capabilities of commercial networks (e.g. documenting supply chains, or eliminating the need for title searches in real estate). You are no more likely to “trust” a realtor or seller with blockchain or without: you are simply more sure of the precise level of impersonal systemic risk of fraud inherent in the business.
Again, the most powerful form of trust is personal. Those who trusted Bernie Madoff were betrayed by Mr. Madoff, not by the system in which he operated. You can reduce systemic risk by regulation — or by blockchain — but the decision to trust an advisor, or anyone for that matter, is ultimately a personal one. You can’t regulate or technologize your way to personal trustworthiness.
Trust words du jour. It is true that consciously altering an organization’s shared vocabulary can have an unconscious effect by nudging people’s perceptions and behaviors — including for trustworthiness. But words alone don’t do the job. In fact, if words are the only effort taken, they can backfire — words are also the favored tool of the best propagandists in history. Context, intent and behaviors also matter.
Words divorced from action — including merely perceived action — actively fuel cynicism. In a world where, broadly speaking, trust is on the decline, cynicism is rising. In the face of cynicism, words without action are predestined to produce the opposite of what was intended. CEO “activism” can also create a “backfire effect” when the words are directed at a third party while the CEO’s headquarters are burning.
Data Security. In most of the Western world (China is a partial outlier on this one), data security is increasingly important. At the simplest level, this is about fear of having our identities stolen and misused with economic consequences. But it also extends to concerns over privacy. It’s tempting to think greater data security adds to trust. But this is the same issue we saw with blockchain, above: a reduction in quantifiable risk is not essentially about trust.
Worse, getting closer to risk-free doesn’t mean we’re increasing trust — it just means lower levels of risk in our trust decisions. Since trusting is essentially a positive inclination to take a risk, higher levels of data security merely remove roadblocks: they don’t say anything about positive levels of trustworthiness. (And by the way, business leaders who have bought in to employee surveillance software are killing any opportunity to build interpersonal trust.)
Chemical Trust. We’re talking about the popularly cited papers on Oxytocin, sometimes called “the trust molecule.” It’s oh so tempting to believe that trust can be reduced to a neuro chemical phenomenon. But there are two powerful reasons to resist that temptation. One is that the early research appears to be just plain wrong. See here, and here, and here. Sorry, folks, it just ain’t true.
And even if it were true — that we could isolate a particular set of chemicals (or synapses, or even genes) which “explain” trust — we likely wouldn’t trust the resulting “trust.” Merely describing something in reductionist physical terms doesn’t account for the full human meaning of trust.
The only practical application of chemical trust would be through chemical induction. But consider: would you trust someone’s declaration of lifelong friendship if they said it under the influence of five martinis? Would you trust your child with the babysitter if said sitter showed up high as a kite on weed?
Defining Trust
So far, we have only nitpicked at “stupid” definitions of trust. It’s time for us to be more proactive, and to put our own stake in the ground.
- Trust is a relationship. It takes two. It doesn’t happen unilaterally; it’s not real until a trusting party meets a trustworthy party.
- At the organizational level, trust must be built one stakeholder at a time, starting internally with employees not customers.
- Organizations don’t build trust — they can only facilitate, or hinder, interpersonal trust. It’s up to the people who work for them, and that begins with leadership.
This means a lot of popular statements are fatally imprecise. If, for example, you see a statement (usually after a survey has been published) like “trust in business is up,” should you infer?
That business is more trustworthy?
That people should trust businesses more?
Or some composite measure of both?
Nonetheless, it is possible to speak more clearly about trust.
- The General Social Survey has for years measured the personal propensity to trust.
- Trusted Advisor Associates has developed the TQ Trust Quotient Self Assessment, which measures personal trustworthiness; and the Four Trust Principles, which are organizational guides to personal behavior in trust-relevant situations.
- Trust Across America’s Trust Alliance has developed Tap Into Trust (now accessed by almost 175,000 people) and its simple AIM (Acknowledge, Identify, Mend) Assessment Tool to identify the behaviors that are building and weakening trust inside and between teams so that they can be directly addressed.
- Doug Conant, the former CEO of Campbell Soup, has created the Conant Flywheel, with “inspiring trust” as the outcome of six drivers. It is noteworthy because it emphasizes the personal nature of trust, and the critical personal role of leaders in creating it.
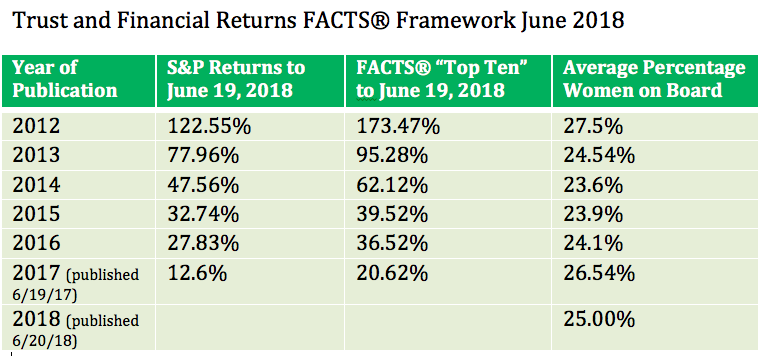
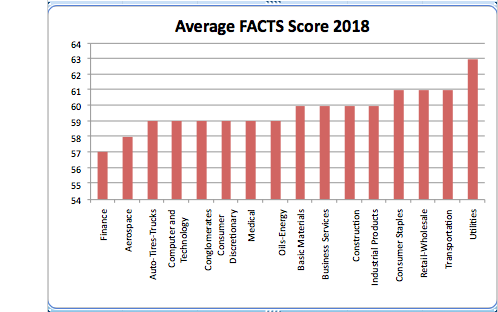
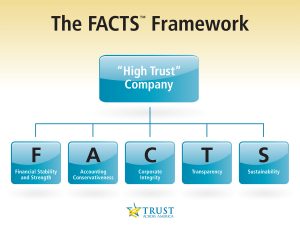
- Trust Across America’s FACTS® Framework has been measuring the “trustworthiness” of public companies for over ten years, making a business case for trustworthiness as an intentional business strategy.
Other great trust models exist for measuring trust at the individual, team and organizational level.
Organizational trust
If, as we have argued all along, personal trust is stronger than institutional trust, then what sense does it make to talk about trust at the corporate level?
That is a very good question, and one that most trust researchers fail to address — it may be the “stupidest” trust trick of all. Merely focusing on corporate reputation, sustainability, “rules” or other corporate attributes does not address the core personal level of trust — the most powerful form, and the one that tends to take a back seat, probably because it requires the most work.
Our definition of organizational trust addresses the issue head on.
A trust-based organization is one in which people behave in trusting and trustworthy manners toward each other, and toward all stakeholders.
The right way to think about trust is that it is all driven and experienced at the personal level: the role of the organization is to help those personal experiences become trust-positive.
Trust Glossary
And finally, we would like to leave you with a glossary that defines the various relational components of trust. While some may believe this adds unnecessary complexity, the definitions can be an important reference when we talk about trust.
Trust: (the noun) is a relationship between trustor and trustee, in the case of individuals. “The level of trust is down.” In its simplest form, some, like Trust Across America, describe it as the outcome of principled behavior.
Trust: (the verb): To trust, or not to trust, the decision to trust, the risks of trusting. “I trust him (or her) (or them).” The field of psychology focuses on this definition.
Trustor: (noun): The one taking the risk, the one choosing to trust — or not to trust. “He trusts them; me, I’m usually more hesitant about it.”
Trustee: (noun) One to whom something is entrusted or the acceptor of the trust. “She’s the one in the group to trust.”
Trustworthy: (adjective) Deserving of confidence based on ethics, competence, dependability and reliability. “He’s highly trustworthy.” “That company is trustworthy.”
Trusting: (gerund) the trust action taken by the trustor. “I’m nervous about trusting them.”
Propensity to trust: An inclination to trust people or institutions. “I leave my car unlocked in the driveway.” “I trust my doctor with my life.” The fields of sociology and group psychology focus on this definition.
____
Barbara Brooks Kimmel is an author, speaker, product developer and global subject matter expert on trust and trustworthiness. Founder of Trust Across America-Trust Around the World she is author of the award-winning Trust Inc., Strategies for Building Your Company’s Most Valuable Asset, Trust Inc., 52 Weeks of Activities and Inspirations for Building Workplace Trust and Trust Inc., a Guide for Boards & C-Suites. She majored in International Affairs (Lafayette College), and has an MBA (Baruch- City University of NY). Her expertise on trust has been cited in Harvard Business Review, Investor’s Business Daily, Thomson Reuters, BBC Radio, The Conference Board, Global Finance Magazine, Bank Director and Forbes, among others.
Charles H. Green is an author, speaker and world expert on trust-based relationships and sales in complex businesses. Founder and CEO of Trusted Advisor Associates, he is author of Trust-based Selling, and co-author of The Trusted Advisor and the Trusted Advisor Fieldbook. He majored in philosophy (Columbia), and has an MBA (Harvard). He has authored articles in Harvard Business Review, Directorship Magazine, Management Consulting News, CPA Journal, American Lawyer, Investments and Wealth Monitor, and Commercial Lending Review.








 Purchase our books at this link
Purchase our books at this link

Recent Comments